|
Octospora leucoloma Hedw. Nat. Arr. Brit. Pl. (London) 1: 667 (1789)
|

| 
|
| 1: Octospora leucoloma, apothecium in turf of Bryum argenteum, Germany, Thuringia, Vogelsberg, leg. Jan Eckstein (59427), 2020-02-14 |
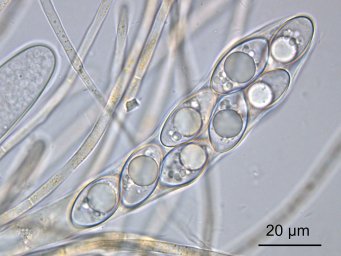
2: Octospora leucoloma, ascus with ascospores |

Apothecia: 1-3 mm in diameter, with weak membranaceous margin or margin somewhat pubescent and slightly elevated, hymeium orange
Asci: 8-spored, spores biseriate
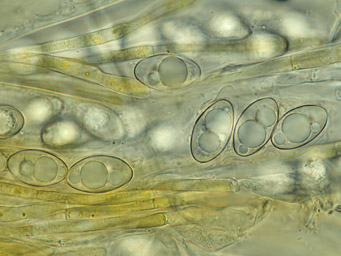
Ascospores: ellipsoid, (18)20-24(26) x (10)11-14 µm, smooth, one or two large and several small oil droplets
Host: Bryum argenteum
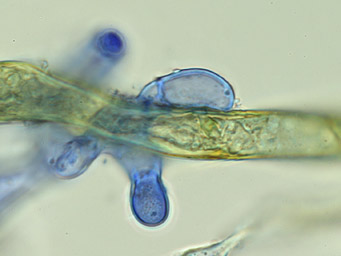
Infectious structures: infects the rhizoids
Habitat: on disturbed soil between shoots of Bryum argenteum
Distribution: known from many European countries, including Austria, France, Germany (common, BY, BE, BB, HH, MV, SN, ST, TH), Hungary, Iceland (Pfister & Eyjólfsdóttir 2007), Spain and North America
Note: specimen with similar spores from other hosts like Bryum dichotomum represent another taxon (Eckstein & Eckstein 2009)

References:
- Benkert, D. 1995. Becherlinge als Moosparasiten. - Boletus 19: 97-127.
- Benkert, D. 1998c. Beiträge zur Kenntnis bryophiler Pezizales-Arten. 8. Viersporige Taxa der Gattung Octospora. - Österreichische Zeitschrift für Pilzkunde. [New series] 7: 39-63.
- Benkert, D. 2007. Zur Kenntnis des Vorkommens bryophiler Pezizales (Ascomycota) in Südost-Europa. - Mycologia Montenegrina 10: 7-21.
- Benkert, D. 2009. Zwei neue Arten bryophiler Pezizales (Ascomycota) aus der Bundesrepublik Deutschland und Auflistung der aus Deutschland bisher nachgewiesenen Arten mit Kurzdiagnostik. - Zeitschrift für Mykologie 75: 51-68.
- Bona, L.M.G. 1982. Contribución al conocimiento de la flora micológica de Navarra: IV. - Anales de la Estación Experimental de Aula Dei. 5–39.
- Boudier, E. 1905-1910. Icones mycologicae ou iconographie des champignons de France principalement Discomycetes. - Paris: Klincksieck.
- Brouwer, E. 1999. Mosschijfjes (Lamprospora en Octospora): voorkomen en verspeiding in Nederland. - Coolia 42: 2-20.
- Caillet, M. & Moyne, G. 1987a. Contribution a l'étude du genre Octospora Hedw. ex S.F. Gray (Pezizales), Espèces à spores elliptiques ou fusiformes. - Bulletin de la Société Mycologique de France 103: 179-226.
- Caillet, M. & Moyne, G. 1991. Clé de détermination du genre Octospora et des genres voisins. - Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire Naturelle du Doubs 84: 9-24.
- Dennis, R. W. G. & Itzerott, H. 1973. Octospora and Inermisia in Western Europe. - Kew Bulletin 28: 5-23.
- Döbbeler, P. 1980a [1979]. Untersuchungen an moosparasitischen Pezizales aus der Verwandtschaft von Octospora. - Nova Hedwigia 31: 817-864.
- Eckstein, J. & Eckstein, G. 2009. Bryoparasitische Pezizales (Ascomycetes) der Gattungen Lamprospora, Octospora und Neottiella im Alten Botanischen Garten von Göttingen. - Herzogia 22: 213-228. PDF (Abstract only)
- Eckstein, J., Eckstein G., Frauenberger, H. & Wieschollek, D. 2020. Erste Checkliste der Moosbecherlinge Thüringens. - Boletus 41: 51-64.
- Engel, H. & Hanff, B. 1985. In Nordwestoberfranken gefundene Arten der Gattung Octospora Hedwig ex S. F. Gray. - Die Pilzflora Nordwestoberfrankens 9/A: 3-20.
- Friebes G., Janošík L., Pöltl M. & Gallé A. 2024. Neue Nachweise bryoparasitischer Pilze in der Steiermark (Österreich). - Joannea Botanik 20: 49–79. PDF
- Fuckel, L. 1866. Ueber rheinische Ascobolus-Arten. - Hedwigia 5: 1-5.
- Hedwig, J. 1789. Descriptio et adumbratio microscopico-analytica Muscorum frondosorum. Tom. II. - Leipzig: J. G. Müller.
- Itzerott, H. 1981. Die Gattung Octospora mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pfälzer Arten. - Nova Hedwigia 34: 265-280.
- Janošík, L., Sochorová, Z., Eckstein, J., Vega, M. & Koukol, O. 2023. Ascospore morphology of bryophilous Pezizales is closely associated with the place of infection and host ecology. - Fungal Ecology 61: 101200. DOI
- Krieglsteiner, L. 2004. Pilze im Biosphären-Reservat Rhön und ihre Einbindung in die Vegetation. - Regensburger Mykologische Schriften 12: 1-770.
- Kristiansen, R. 2006. Miniatyrbegersopper nye for Norge. - Agarica 26: 69-77.
- Kullman, B. 1991. Octospora tetraspora as a four-spored O. leucoloma? - Cryptogamic Botany 2/3: 115-117.
- Németh, C. 2020. Bryophilous ascomycetes (Pezizales) in Hungarian cemeteries. - Herzogia 33: 319-339.
- Pfister D.H. & Eyjólfsdóttir G. G. 2007. New records of cup-fungi from Iceland with comments on some previously reported species. - Nordic Journal of Botany 25: 104–112.
- Ribollet, P. 2015. Contribution a? la connaissance des genres Octospora Hedw. 1789 et Lamprospora De Not. 1864 en Loire-Atlantique. - Cahiers Mycologiques Nantais 27: 3-12. PDF
- Rifai, M. A. 1968. The Australian Pezizales in the Herbarium of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. - Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen Afdeling Natuurkunde Tweede Reeks 57 (3): 1-295.
- Rubio, E., Suárez, A. & Miranda, M. A. 2000. El genero Octospora Hedw.:S.F. Gray (Ascomycetes, Pezizales) en Asturias y Leon. - Bol. Soc. Micol. Madrid 25: 111-126.
- Rubio, E. & Miranda, M. A. 2006. Estudios micológicos en el Parque Natural de Somiedo (Asturias). II Campaña. Ascomycota. - Boletín de la Sociedad Micológica de Madrid 30: 49–72.
- Seaver, F. J. 1928. The North American cup-fungi (Operculates). - New York.
- Vega, M. 2017. Vorläufige Checkliste der in Hamburg vorkommenden Moosbecher-Arten aus den Gattungen Lamprospora, Neottiella, Octospora und Octosporopsis. - Boletus 38: 27-33.
- Yao, Y. J. & Spooner, B. M. 1996b. Notes on British species of Octospora. - Mycological Research 100: 175-178.
|
| Images:
|

|
|
| 3: Octospora leucoloma, apothecium in turf of Bryum argenteum |
4: Octospora leucoloma, ascospores, Germany, Thuringia, Vogelsberg, leg. Jan Eckstein (59427), 2020-02-14 |
|
|
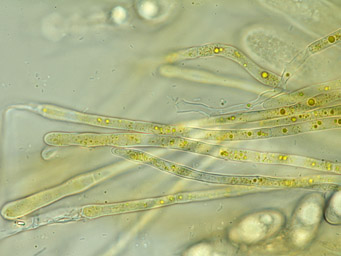
| 5: Octospora leucoloma, paraphyses, Germany, Thuringia, Vogelsberg, leg. Jan Eckstein (59427), 2020-02-14 |
6: Octospora leucoloma, infection, Germany, Thuringia, Vogelsberg, leg. Jan Eckstein (59427), 2020-02-14 |

|
|



